The importance of maintaining pool water balance cannot be overstated. It is the cornerstone of a healthy and enjoyable swimming environment. Balanced water not only ensures the longevity of pool equipment but also protects the health of swimmers and maintains water clarity. Achieving this balance requires a thorough understanding of the various water chemistry factors and their impact on the pool ecosystem. By keeping these factors in balance, pool owners can prevent common problems such as corrosion, scaling, and uncomfortable swimming conditions.
Understanding Pool Water Balance
Pool water balance is the balance of chemical conditions in the pool water where it is neither too acidic nor too basic. This balance is critical to the effectiveness of sanitizers, the protection of pool surfaces and equipment, and the comfort of swimmers.
Factors Affecting Water Balance
Several key factors affect the balance of pool water: pH, total alkalinity, calcium hardness, temperature, and total dissolved solids. Each of these plays a key role in maintaining ideal swimming conditions:
- pH determines the acidity or basicity of the water. A balanced pH level (usually between 7.2 and 7.8) is necessary for chlorine to work effectively and for swimmers to be comfortable.
- Total alkalinity acts as a pH buffer, preventing sudden fluctuations in pH. The ideal level is between 80 and 120 ppm.
- Calcium hardness is the amount of dissolved calcium in the water. The correct level (200-400 ppm) prevents plaster damage and scale formation.
- Temperature affects chemical reactions and comfort levels. Warmer water may require more chlorine.
- Total dissolved solids (TDS) is the sum of all the chemicals in the pool. High levels can reduce sanitizer effectiveness and water clarity.
Calculate Pool Volume
Understanding your pool’s volume is critical for applying the correct dosage of chemicals. Here’s how to calculate the volume for different pool shapes:
Impact of Volume on Chemical Dosage and Efficiency
The volume of your pool directly affects how much of each chemical you need to use to achieve balance. Accurate calculations ensure effective sanitation without overuse of chemicals, which can be costly and potentially harmful.
Rectangular or Square Pool Formula
To calculate the volume of a rectangular or square pool, multiply the length by the width by the average depth. The formula is
Volume = Length x Width x Average Depth x 7.5 (for gallons).
Round or Circular Pool Formula
For a round or circular pool, the formula is:
Volume = Diameter x Diameter x Average Depth x 5.9 (for gallons).
Oval Pool Formula
Calculate the volume of an oval pool using:
Volume = Length x Width x Average Depth x 5.9 (for gallons).
Kidney-Shaped Pool Formula
Kidney-shaped pools require a bit more calculation, generally estimated as:
Volume = (Length x Width x Average Depth) x 7.0 (for gallons), considering the irregular shape.
You can use a pool volume calculator if you have trouble with the calculations: swimmingpool.com/resources/tools&apps/pool-volume-calculator/
Tools and Supplies Needed
Maintaining a pool requires a set of specific tools and supplies to ensure the water is safe for swimming. Understanding what you need is the first step in effective pool maintenance.
List of Essential Testing Kits and Tools for Measuring Water Balance
To keep your pool’s water in check, you’ll need the following testing kits and tools:
- pH Test Strips: To measure the acidity or alkalinity of the water.
- Chlorine Test Kits: To determine the chlorine levels, ensuring they are within the safe range for swimming but effective enough to kill bacteria and algae.
- Total Alkalinity (TA) Test Kits: To measure the water’s ability to resist pH changes.
- Calcium Hardness Test Kits: To assess the levels of calcium in the water, which can affect the pool’s surfaces and water clarity.
- Cyanuric Acid Test Kits: To measure the stabilizer level that protects chlorine from being quickly degraded by sunlight.
Introduction to Chemical Adjusters Needed to Correct Imbalances
Once you’ve tested your water, you may need to adjust its balance using various chemicals:
- pH Increasers and Decreasers: To adjust the water’s pH to the ideal range of 7.2 to 7.8.
- Alkalinity Increasers: To raise total alkalinity and stabilize pH levels.
- Calcium Hardness Increasers: To prevent pool surfaces from becoming damaged.
- Cyanuric Acid: To stabilize chlorine levels and make them more effective under the sun.
- Chlorine and Non-Chlorine Shock: To kill bacteria, algae, and other organic matter.
Safety Equipment and Precautions When Handling Pool Chemicals
Handling pool chemicals requires caution. Always use:
- Protective Gloves and Goggles: To protect your skin and eyes from chemical burns.
- Long-Sleeved Clothing: To protect your skin from splashes.
- Proper Ventilation: When handling chemicals avoid inhaling fumes.
Remember to store chemicals in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight, and never mix different chemicals together.
Testing Your Pool Water
Regular testing of your pool water is vital to maintain its cleanliness, safety, and longevity.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Test Pool Water Using Test Strips and Liquid Test Kits
- Collect a Water Sample: For liquid kits, fill the vial with water from at least 18 inches below the surface. For strips, simply dip them into the water.
- Apply Reagents (If Using a Liquid Kit): Add the reagents to the sample as per the instructions.
- Dip the Test Strip: If using strips, dip them into the water sample for the time specified by the manufacturer.
- Compare Results: Match the color of the strip or sample to the color chart provided with your kit.
Understanding Test Results and What They Indicate About Your Pool’s Water Balance
- pH Level: Indicates the acidity or alkalinity. The ideal range is 7.2 to 7.8.
- Chlorine Level: Shows the disinfectant level. Ideally between 1-3 ppm.
- Total Alkalinity: The ideal range is 80-120 ppm, which helps stabilize pH levels.
- Calcium Hardness: Ideal levels are 200-400 ppm to prevent plaster damage.
- Cyanuric Acid: Should be kept between 30-50 ppm to protect chlorine from sunlight.
Frequency of Testing for Optimal Pool Maintenance
- pH and Chlorine: Test at least twice a week.
- Total Alkalinity: Test weekly.
- Calcium Hardness and Cyanuric Acid: Test monthly
Adjusting pH Levels
Maintaining the correct pH level in your pool is essential for the health of the pool, the comfort of its users, and the effectiveness of the disinfectants used. This section will guide you through the importance of pH levels, how to adjust them, and tips to prevent fluctuations.
Importance of Maintaining the Correct pH Level for Pool Health
The pH level of your pool water affects every aspect of the pool’s environment. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Pool water is best kept slightly alkaline, between 7.2 and 7.8. This range ensures:
- Optimal Disinfectant Efficiency: Chlorine and other disinfectants work best within this pH range.
- Swimmer Comfort: Prevents eye and skin irritation.
- Equipment Preservation: Prevents corrosion of pool components and damage to the pool liner or finish.
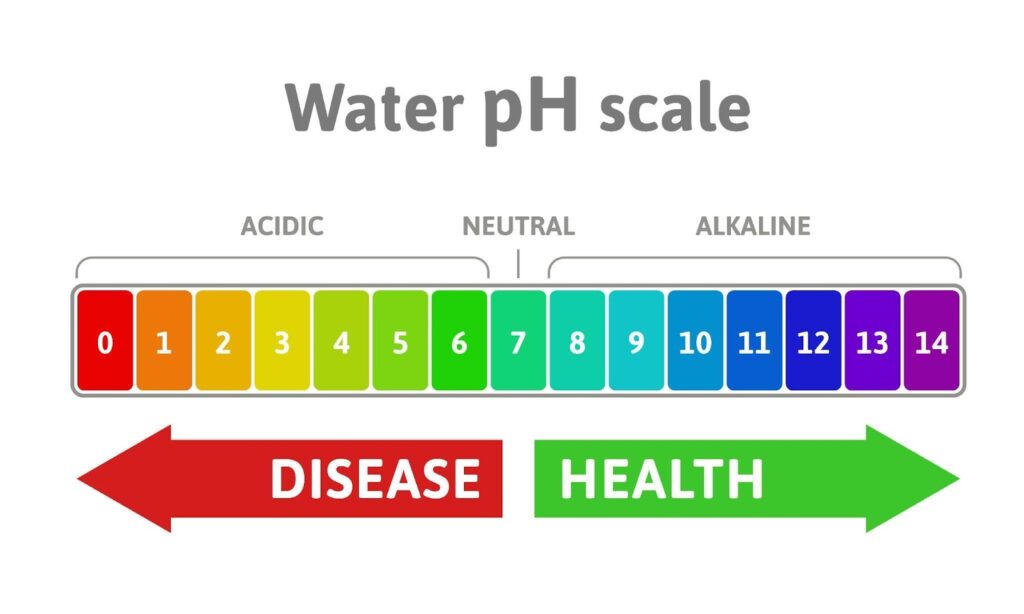
Maintaining the correct pH is thus crucial for the overall health of your pool and those who use it.
How to Raise or Lower pH Levels Using Chemical Adjusters
To adjust the pH levels in your pool, you will use either pH increasers (to raise the pH) or pH decreasers (to lower the pH). Here’s how to do it:
- To Raise pH: Use a pH increaser, typically soda ash (sodium carbonate). Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the correct amount to add based on your pool’s volume and the current pH level. Add the increaser slowly to the pool, preferably in the deep end to allow for better distribution.
- To Lower pH: Use a pH decrease, such as muriatic acid or sodium bisulfate. Similar to raising pH, follow the instructions on the product label for dosage amounts. When adding muriatic acid, it’s advisable to pour it into the pool while walking around the perimeter to ensure even distribution.
For specific instructions on raising pH without affecting alkalinity, resources like the video “How to Raise pH in Your POOL” by Swim University provide detailed guidance. These resources often recommend precise techniques and amounts to adjust pH levels effectively while maintaining stable alkalinity.
Tips for Preventing pH Fluctuations
Preventing pH fluctuations is key to maintaining pool health and reducing the need for constant adjustments. Here are some tips:
- Regular Testing: Monitor your pool’s pH level frequently to catch and correct minor fluctuations early.
- Balanced Alkalinity: Maintain total alkalinity within the recommended range of 80-120 ppm to help stabilize pH levels.
- Proper Chemical Addition: When adding chemicals to your pool, do so gradually and in the recommended manner to avoid sudden pH changes.
- Control Runoff: Prevent garden chemicals, fertilizers, and other substances from entering the pool, as these can alter the pH level.
- Consistent Maintenance: Regularly clean your pool and filter system to prevent organic matter from affecting pH levels.
This video will help you to know How to raise the pH in Your Pool
Managing Total Alkalinity
Total alkalinity is the most important factor in pool water chemistry, serving as the basis for pH stability and overall water balance. Proper management of total alkalinity is essential to maintaining a healthy pool environment. In this section, we will look at what total alkalinity is, how it affects pH stability, how to manage it, and how it relates to pH balance.
Explanation of Total Alkalinity and Its Impact on pH Stability
Total alkalinity (TA) measures the concentration of alkaline substances in the water. It acts as a buffer, absorbing fluctuations in pH to maintain stability. The ideal range for total alkalinity in pool water is between 80 to 120 parts per million (ppm). When TA levels are within this range, it helps prevent rapid and wide variations in pH, ensuring a more stable pool environment. This stability is crucial for the effectiveness of disinfectants, the comfort of swimmers, and the protection of pool surfaces and equipment.
Guidelines for Adjusting Total Alkalinity Levels
Adjusting total alkalinity is a fundamental aspect of pool maintenance. Here are steps to increase or decrease TA levels:
- To Increase Total Alkalinity: Use an alkalinity increaser, which is typically sodium bicarbonate. Add the recommended amount based on your pool’s volume and the current alkalinity level. Distribute the increaser evenly around the pool, then allow the pump to circulate the water to evenly distribute the chemical.
- To Decrease Total Alkalinity: Use muriatic acid or sodium bisulfate. These chemicals should be added slowly, in a well-ventilated area, and preferably with the pool pump running to ensure proper mixing. The amount required depends on the current alkalinity level and the pool’s volume. It’s often recommended to add the chemical in stages, testing the water after each addition, to avoid lowering the alkalinity too much.
After adjusting total alkalinity, including taking steps to reduce pool alkalinity if necessary, wait 24 to 48 hours before retesting the water to allow the chemicals to fully integrate and the levels to stabilize. This ensures that the pool water remains in the ideal range for total alkalinity, contributing to a stable and balanced pool environment.
Relationship Between Total Alkalinity and pH Balance
Total alkalinity and pH balance are closely linked aspects of pool chemistry. Total alkalinity serves as a buffer for pH, helping to absorb changes and maintain stability. When alkalinity is within the correct range, it’s much easier to control and maintain pH levels within their ideal range (7.2 – 7.8). However, if total alkalinity is too low, the pool water becomes susceptible to “pH bounce,” where the pH level fluctuates widely and unpredictably. If alkalinity is too high, it can lead to a condition known as “pH lock,” where adjusting the pH becomes difficult, and the water can become cloudy due to the high alkaline content.
Calcium Hardness Control
Importance of Calcium Hardness in Preventing Plaster Damage and Water Cloudiness
Calcium hardness refers to the amount of dissolved calcium in the pool water. It’s crucial for preventing plaster damage in concrete pools and water cloudiness. Ideal levels help protect pool surfaces from etching or scaling and ensure clear water. The recommended calcium hardness level is between 200-400 parts per million (ppm).
How to Adjust Calcium Hardness Levels in Your Pool
To increase calcium hardness, add a calcium chloride product according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Dissolve the granular product in water before adding it to the pool to prevent cloudiness. To decrease calcium hardness, it’s more challenging as it often requires diluting the pool water with softer water or using a flocculant and then physically removing the precipitated calcium.

Strategies for Dealing with Too-High or Too-Low Calcium Hardness
For High Calcium Hardness: Partially drain and refill the pool with softer water or use a chelating agent to bind the calcium.
- For Low Calcium Hardness: Add calcium chloride to increase the level, ensuring to dissolve it properly before introduction to the pool.
- For detailed information on managing calcium hardness, refer to resources like Frog Products’ guide at FrogProducts.com.
Addressing Temperature and Total Dissolved Solids
The Effect of Temperature on Chemical Effectiveness and Swimmer Comfort
Temperature influences both the effectiveness of pool chemicals and swimmer comfort. Warmer water accelerates chemical reactions, affecting disinfectant levels and increasing the risk of algae growth. It also impacts swimmer comfort.
Understanding Total Dissolved Solids and Their Impact on Water Quality
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) measure all organic and inorganic materials in the pool, affecting water clarity and quality. High TDS levels can reduce the effectiveness of disinfectants and lead to water that feels “hard”.
Methods to Manage Temperature Fluctuations and Reduce Total Dissolved Solids
- Temperature Management: Use pool covers to minimize heat loss during cooler months and to reduce excessive warming by the sun.
- Reducing TDS: Regularly drain and add fresh water to lower TDS levels, especially in areas with high mineral content in the water supply.
Routine Maintenance for Balanced Pool Water
Daily, Weekly, and Monthly Maintenance Tasks to Keep Pool Water Balanced
- Daily: Check and adjust pH and chlorine levels.
- Weekly: Test total alkalinity, calcium hardness, and cyanuric acid levels. Clean pool walls and floor.
- Monthly: Check TDS and inspect pool equipment.
The Role of Pool Covers, Filtration, and Circulation in Maintaining Balance
- Pool Covers: Reduce evaporation and debris entry.
- Filtration and Circulation: Remove contaminants and distribute chemicals evenly.
Seasonal Adjustments for Pool Water Balance
Adjust chemical levels and cleaning frequency based on seasonally changing conditions, such as increased use in summer or cooler temperatures in winter.
Troubleshooting Common Pool Water Balance Issues
Identification and Solutions for Common Problems
- Algae Blooms: Increase chlorine levels and brush the pool walls.
- Cloudy Water: Check and adjust the filtration system, and consider flocculant.
- Chlorine Inefficiency: Adjust stabilizer levels and shock the pool if necessary.
How to Reset Your Pool Water Balance in Extreme Cases
In extreme cases, such as severe chemical imbalances or contamination, it may be necessary to partially or fully drain the pool and start fresh.
This guide has covered essential aspects of maintaining pool water balance, from calcium hardness to routine maintenance. Regular upkeep is the key to enjoying a safe and sparkling pool. We encourage regular maintenance and invite feedback and questions from readers to ensure your pool remains a source of joy and relaxation.
By adhering to the guidelines and tips provided, you can prevent common issues and ensure your pool water remains balanced and healthy, providing a safe and enjoyable environment for all swimmers.




