With the growing popularity of swimming as a recreational and fitness activity, the importance of pool safety cannot be overemphasized. Among various concerns, the issue of swimming during illness has attracted particular attention. This article focuses on the complexities associated with water sports during common illnesses and aims to provide important guidance on how to swim responsibly in these waters. Understanding the risks associated with swimming during illness will not only protect the individual but also preserve the health of the entire community that visits these water bodies. Understanding the Risk of Swimming While Sick
Understanding the Risk of Swimming While Sick
How Illnesses Can Spread in Pool Environments
Swimming pools, despite being treated with chlorine and other disinfectants, can become hotspots for a variety of pathogens if proper hygiene practices are not followed. Diseases can spread through water in a variety of ways, including through skin scales, bodily fluids, or direct contact with contaminated surfaces. If an infected person swims in a shared pool, they risk passing the disease to others, which can lead to an outbreak.
Overview of Common Waterborne Illnesses and Their Symptoms
Waterborne diseases often present with a range of symptoms from mild skin irritation to serious gastrointestinal disorders. Common diseases include Cryptosporidium, Giardia, and E. coli infections, which manifest as diarrhea, vomiting, and fever. Other diseases such as swimmer’s ear and skin rashes are also common. Recognizing these symptoms is critical for timely treatment and preventing further spread of infection.
Discussing the Potential Impact on Other Pool-Goers
The presence of sick people in a swimming pool can have a domino effect, affecting many other people. Vulnerable groups such as children, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems are particularly at risk. The public nature of swimming pools requires a collective effort to maintain hygiene to protect everyone’s health.
Specific Illnesses and Swimming
Cold and Flu: Can You Swim with Respiratory Symptoms?

Swimming with a cold or flu is not recommended. Respiratory symptoms may be exacerbated by the strain on the body while swimming, and there is a high risk of transmitting the virus to others. In addition, chlorinated water can irritate the respiratory tract, aggravating symptoms.
Gastrointestinal Issues: Risks Associated with Swimming While Experiencing Stomach Problems
Individuals experiencing gastrointestinal issues, especially those with symptoms like diarrhea, should avoid swimming pools. The risk of contaminating the water with pathogens that cause stomach illnesses is significant, and these pathogens can be highly resistant to chlorine, making them difficult to eliminate once in the pool.
Contagious Skin Conditions: When to Avoid Swimming to Prevent Transmission
Contagious skin diseases such as ringworm, impetigo, and molluscum contagiosum require refraining from swimming to avoid spreading infection. These diseases are easily transmitted by direct contact with contaminated water or surfaces around the pool. It is extremely important for people with visible skin infections to stay out of the water until they have fully recovered.
COVID-19 and Swimming Pools: Specific Considerations
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, swimming pools have become places that require special attention because they can become crowded places. Understanding how the virus is transmitted and measures that can prevent its spread is critical to making aquatic activities safer for all participants.
COVID-19 primarily spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. It can also spread by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus and then touching the face. In pool settings, the risk of transmission through water is low, thanks to the disinfectant properties of chlorine. However, the real danger lies in close contact with others around the pool area, shared surfaces like deck chairs and handrails, and enclosed spaces such as changing rooms.
Prevention measures include maintaining physical distance, wearing masks when not in the water, regular hand washing, and disinfecting commonly touched surfaces. Pool operators are also advised to limit the number of people in the pool at any given time and ensure proper ventilation in indoor spaces.
Guidance On Social Distancing And Crowd Management Around Pools
Social distancing is a key strategy for reducing the risk of COVID-19 transmission. Pool operators should enforce rules that require individuals or family groups to stay at least 6 feet apart, both in and out of the water. This may include marking space on the pool deck, limiting the number of lounge chairs, and controlling entry to avoid overcrowding.
Introducing time slots for pool access can help regulate the number of people in the pool at any given time, ensuring everyone can enjoy the water while maintaining a safe distance from others. For vulnerable groups, such as the elderly or those with weakened immune systems, special hours can be set aside to provide them with a safer environment.
The Role Of Masks And Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) In Pool Settings
Although wearing masks in the water is not recommended for safety reasons, they should be worn in the pool when social distancing cannot be maintained. This is particularly important in common areas such as the entrance, changing rooms and toilets. Staff should also wear appropriate PPE, including masks and gloves when interacting with guests or handling items that may be shared.
Pool operators can further reduce risks by installing hand sanitizing stations, encouraging their use when entering and leaving the pool, and posting signs reminding visitors of the importance of wearing masks, hand hygiene and keeping their distance from others.
General Guidelines for Pool Safety
Swimming pools, both public and private, serve as recreational and exercise centers for people of all ages. However, the use of these facilities comes with the responsibility to ensure safety for oneself and others. Following established pool safety guidelines is paramount to preventing accidents and maintaining a healthy swimming environment.
Pool rules and regulations are established to protect swimmers from harm. They may include guidelines for appropriate swimwear, restrictions on running or diving in certain areas, and prohibitions on rough play, or alcohol consumption. Adherence to these rules is necessary to minimize the risk of injury and ensure safe pool attendance for all swimmers. Pool patrons should familiarize themselves with these rules, which are often posted around the pool, and abide by the boundaries they set.
Emphasizing the Need for Personal Hygiene Before Entering the Pool
Personal hygiene plays a critical role in preventing the spread of infections in swimming pools. Showering before visiting the pool helps remove sweat, makeup and other contaminants that can affect water quality. Encouraging swimmers to use restrooms as needed and to avoid the pool completely if symptoms of illness appear is also a key practice in maintaining a hygienic swimming environment. Pool operators can support these efforts by providing clean and accessible showers and changing rooms.
Ensuring Proper Supervision, Especially for Children and Inexperienced Swimmers
Drowning poses a significant risk, especially for children and those who cannot swim. To prevent accidents, constant and attentive supervision is necessary. Parents, guardians or designated adults should keep children at arm’s length at all times and not be distracted by other activities in the pool. Those who do not swim and those learning to swim should consider the use of flotation devices, although they are no substitute for vigilant supervision.
Brief Discussion on the Role of Lifeguards and Their Responsibilities
Lifeguards play a vital role in pool safety: they are tasked with monitoring the well-being of swimmers and enforcing pool rules. Their training enables them to recognize signs of distress, perform rescue operations, and administer first aid, including CPR if necessary. Swimmers must respect the authority of lifeguards and follow their instructions quickly. However, the presence of lifeguards does not negate the need for personal responsibility and parental supervision. It is a cooperative effort to ensure safe swimming for all.
Safety Measures in Swimming Areas: Review of Standard Pool Safety Measures
Safety in swimming areas goes beyond personal vigilance and involves a comprehensive approach to preventing accidents and health problems. Standard pool safety measures include installing physical barriers such as fencing to prevent unattended access, especially by children. Clear signage indicating the depth of the pool, areas where diving is not allowed, and emergency procedures are very important. The availability of life-saving equipment such as lifebuoys and poles and first aid kits are also part of these important measures. Regular safety drills and staff training ensure that you are prepared for any emergency.
Chlorine and Its Effectiveness Against The Virus
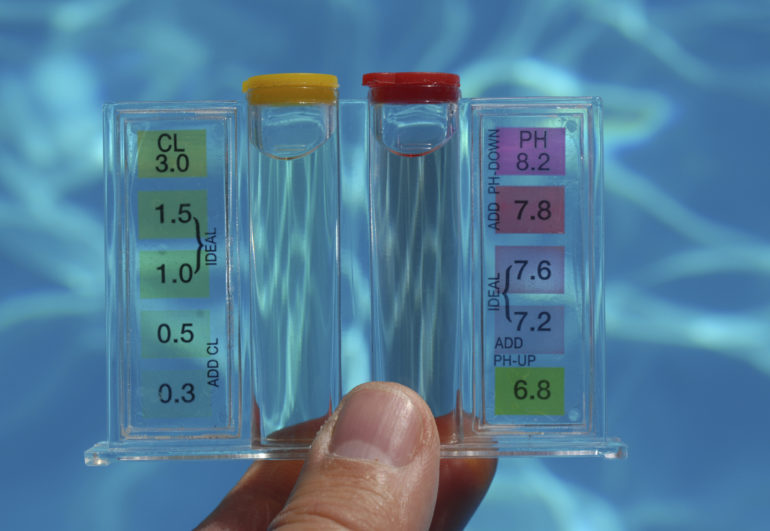
Chlorine is a powerful disinfectant widely used in pool maintenance to kill bacteria and viruses, including the pathogen that causes COVID-19. When recommended levels (1-3 parts per million for swimming pools) are met, chlorine effectively inactivates the virus, greatly reducing the risk of waterborne transmission. However, it is important to balance chlorine levels to maintain water safety without causing irritation to swimmers’ skin and eyes. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of chlorine and pH levels is vital to ensure pathogen control effectiveness and comfortable swimming conditions.

Importance of Proper Hygiene Practices
Proper hygiene is the basis for preventing the spread of infections in swimming areas. This includes showering before visiting the pool to remove dirt, oils and possible pathogens from the skin. Swimmers should also avoid the pool during illness, especially those with gastrointestinal symptoms, to avoid contaminating the water. Encouraging the use of waterproof diapers for infants and toddlers and regular toileting can also reduce the risk of waterborne illness. Hand hygiene provided by accessible handwashing stations also contributes to maintaining a clean swimming environment.
Importance of Regular Maintenance and Water Quality Testing
Regular maintenance and water quality checks are critical to identifying and reducing risks in swimming pools. This includes checking chlorine and pH levels daily to ensure they remain within safe limits, and regularly inspecting pool equipment and surfaces for wear, damage or contamination. Testing for pathogens, including bacteria and viruses, helps assess the overall health risk to swimmers. Routine cleaning and maintenance, including changing filters and sanitizing surfaces, are necessary to prevent the accumulation of contaminants and keep the pool safe for everyone.
Swimming pools provide invaluable health benefits and recreational opportunities, but their enjoyment comes with a responsibility toward personal and public health. By adhering to the outlined safety measures and guidelines, individuals can contribute to a safer swimming environment, mitigating the risks associated with illnesses and ensuring a healthy, enjoyable experience for all.




